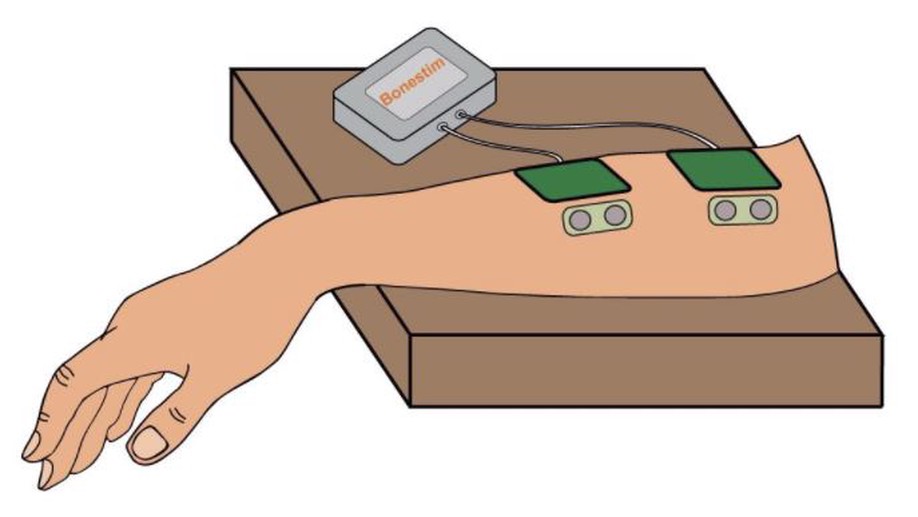
Intensity and Dose of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Influence Sensorimotor Cortical Excitability
Study about the relevance of intensity and dose of NMES, and how these parameters can influence the recruitment of the sensorimotor pathways from the muscle to the brain.
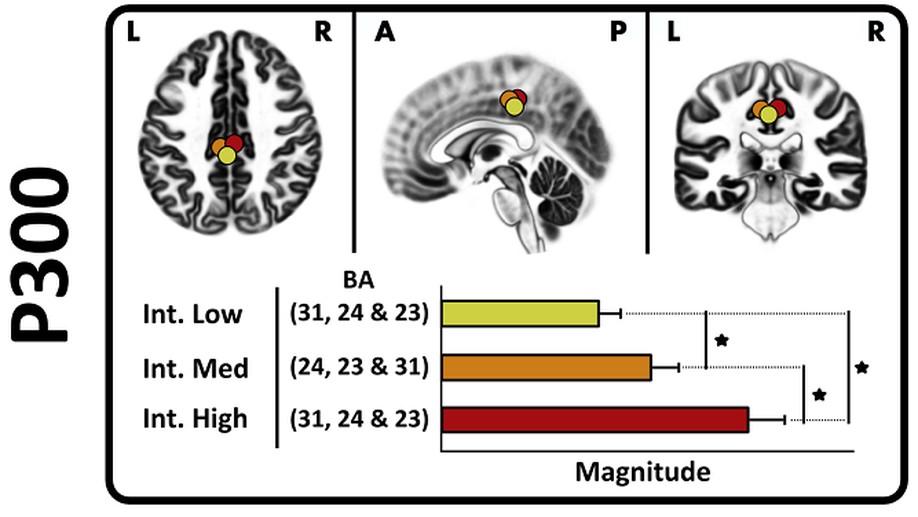
Brain signatures of afferent mismatch during neuromuscular electrical stimulation
Neurophysiology analysis of the EEG correlates elicited as the results of random and unexpected disturbances along different time points of somatosensory stimulation.
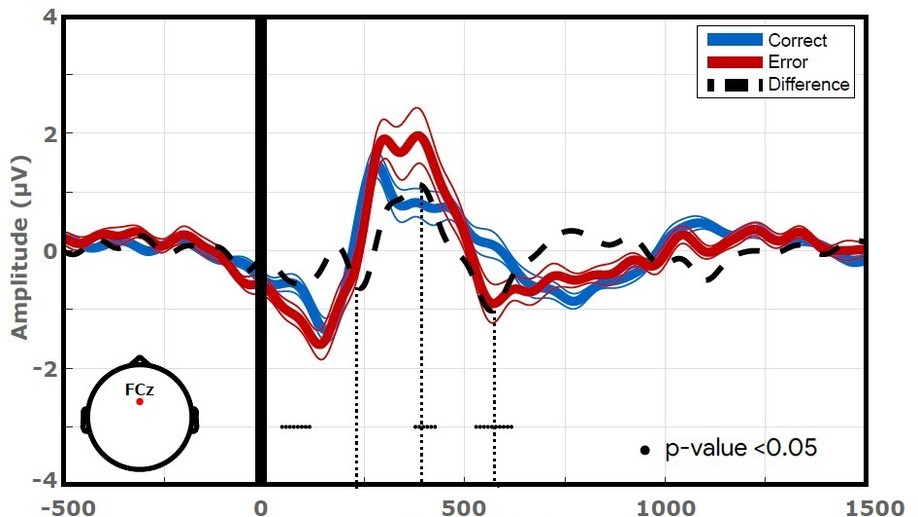
Factors that affect error potentials during a grasping task: toward a hybrid natural movement decoding BCI
Study on how to combine neural correlates of natural movements and interaction error-related potentials (ErrP) to perform a 3D reaching task, focusing on the impact that such factors have on the evoked ErrP signatures and in their classification.
Hierarchical decoding of grasping commands from EEG
A hierarchical method to asynchronously discriminate two different grasps often used in daily life actions (palmar, pincer) from a combined set of motor execution and motor intention.
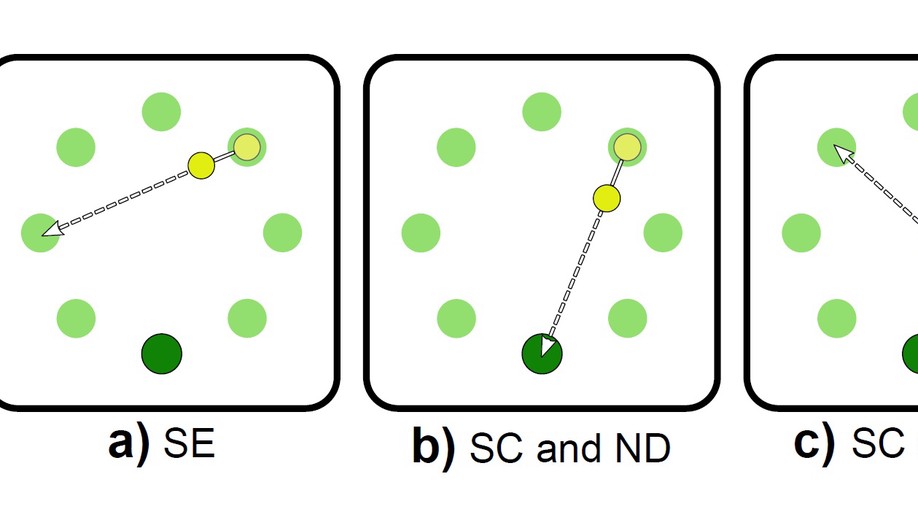
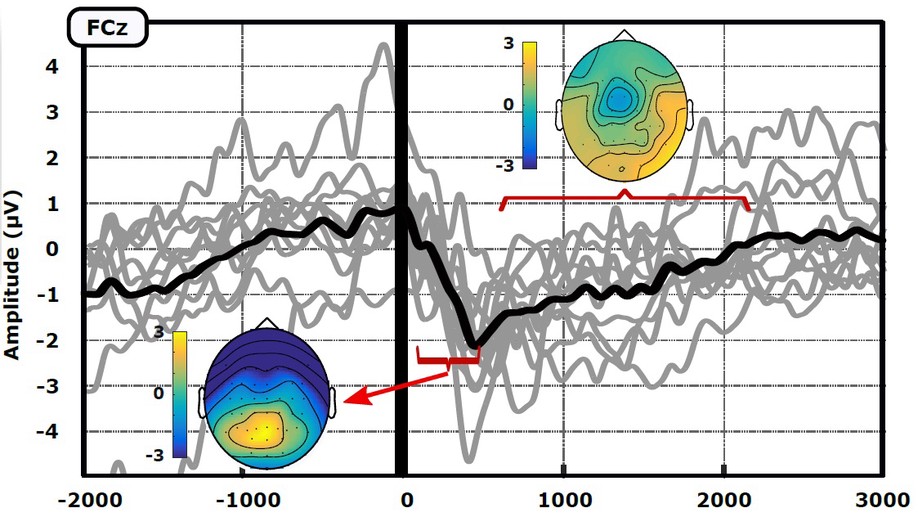
Asynchronous Decoding of Error Potentials During the Monitoring of a Reaching Task
We demonstrate the existence of neural correlates for two types of elicited error potentials (errors at the beginning of a movement, and errors in the middle of a trajectory), and we are able to asynchronously detect them with high accuracies.
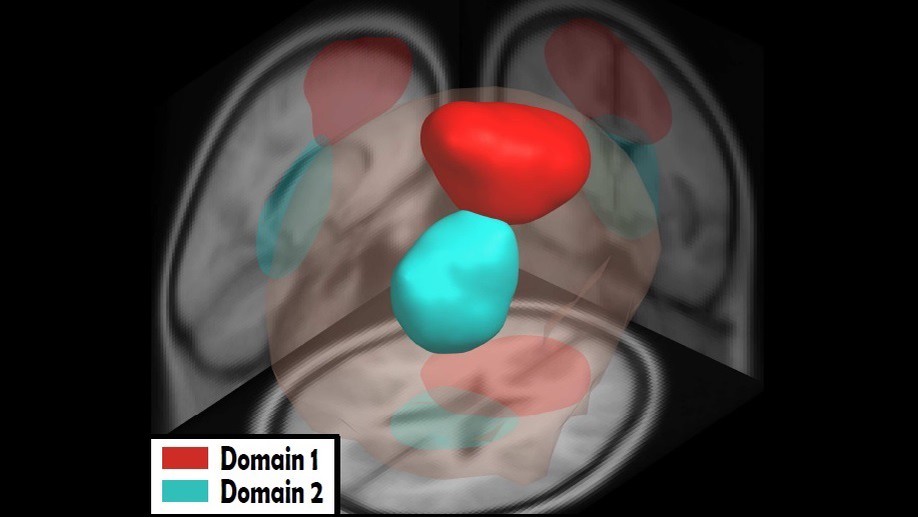
Analysis and asynchronous detection of gradually unfolding errors during monitoring tasks
Application of transfer learning to asynchronously detect gradual errors from EEG signals during a continuous trajectory monitoring task and post-hoc analysis of the decoded neural correlates.
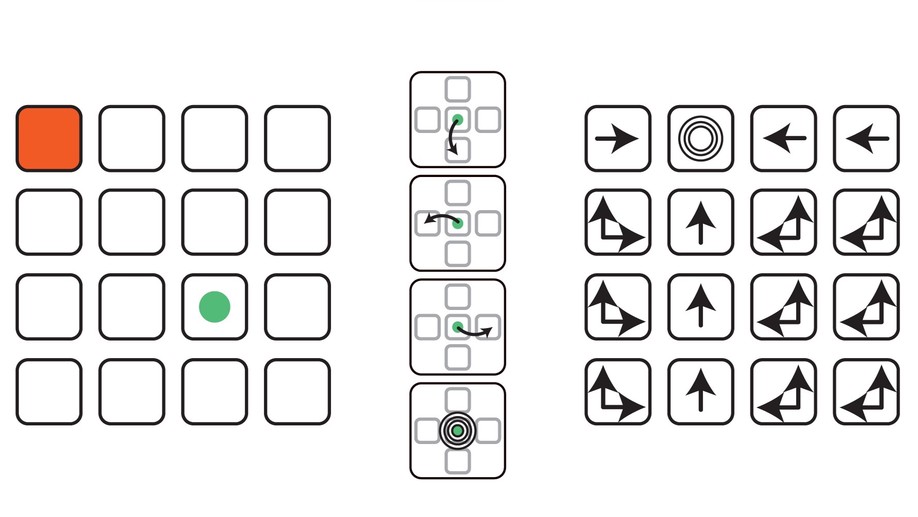
Exploiting Task Constraints for Self-Calibrated Brain-Machine Interface Control Using Error-Related Potentials
New approach for self-calibration BCI for reaching tasks using error-related potentials.
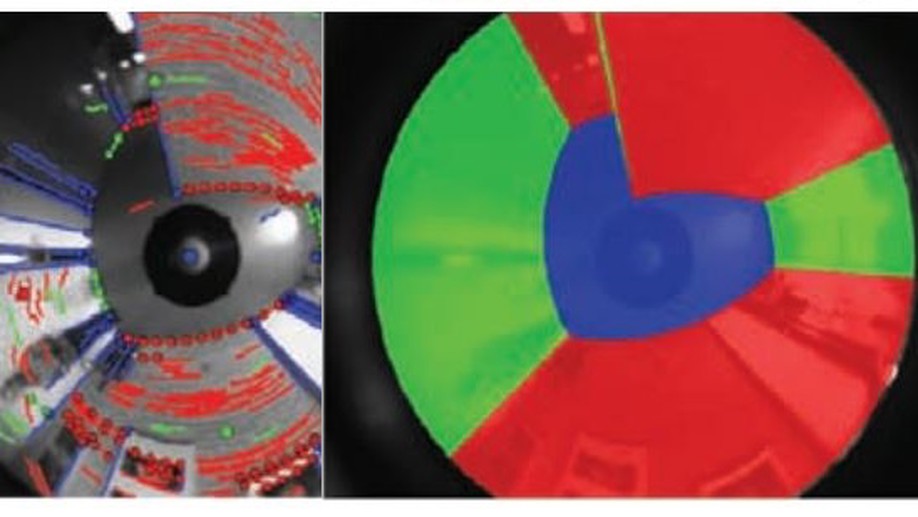
Spatial layout recovery from a single omnidirectional image and its matching-free sequential propagation
New method to recover the spatial layout of indoor environments from omnidirectional images assuming a Manhattan world structure and a matching-free propagation along a sequence of images based on homographies.
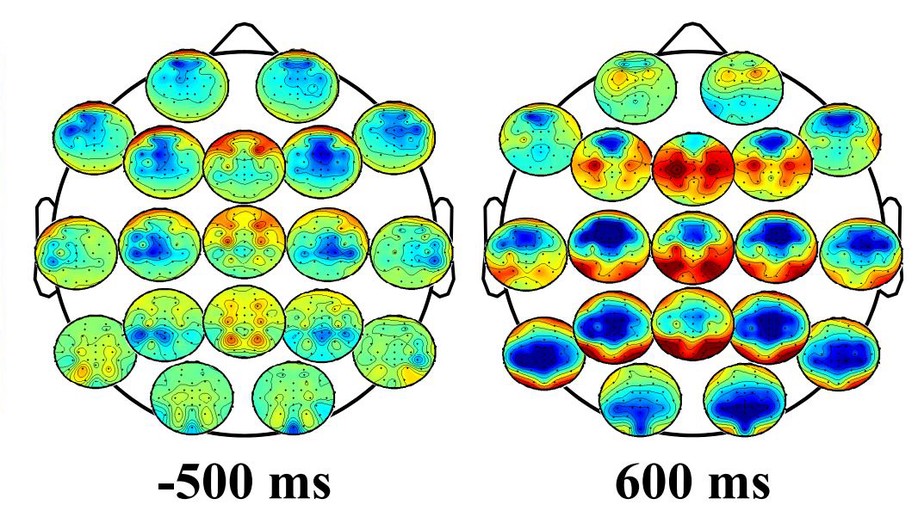
Brain connectivity in continuous error tasks
Study of brain connectivity coherence patterns in EEG during continuous monitoring tasks as an alternative feature to be exploited by asynchronous ErrP detectors.
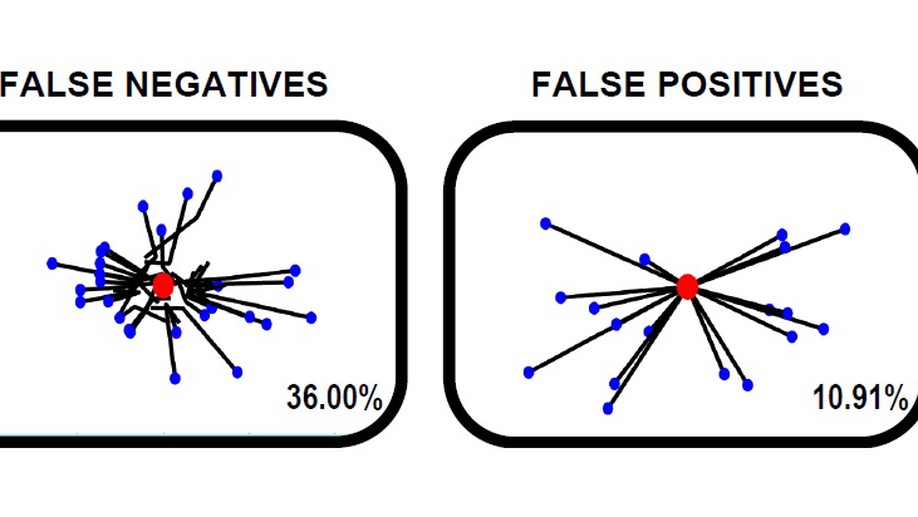
Asynchronous detection of error potentials
Experimental protocol that allows to train a decoder and detect errors in single trial using a sliding window.
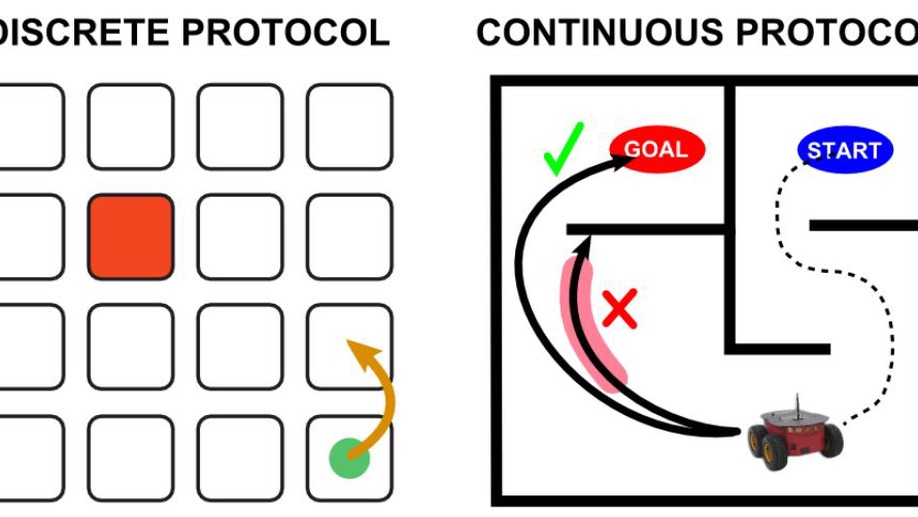
Detection of event-less error related potentials
First study towards the detection of error-related potentials from EEG measurements during continuous trajectories performed by a virtual device.
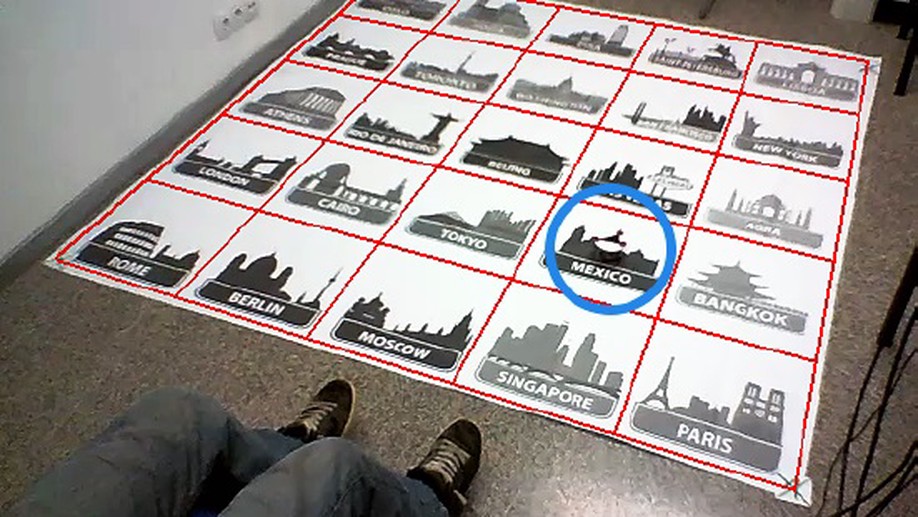

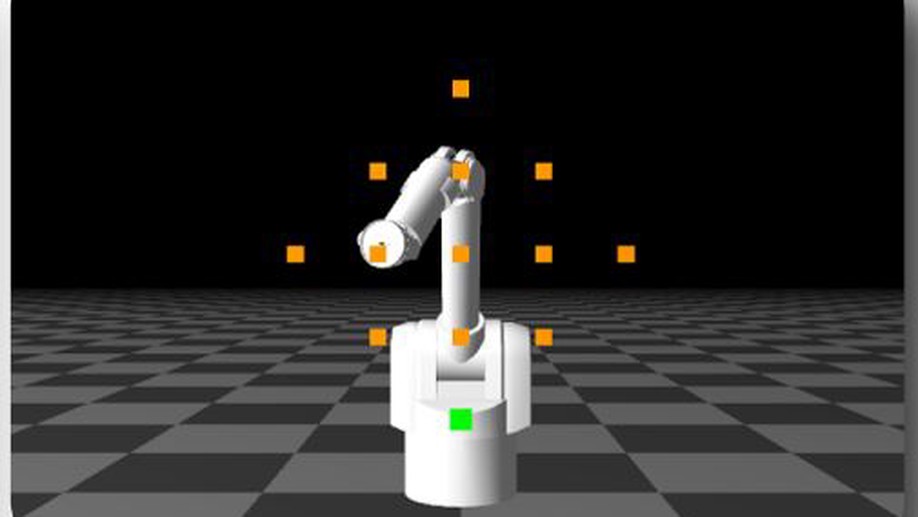
Shared control of a robot using EEG-based feedback signals
An algorithm based on policy matching for inverse reinforcement learning to infer the user goal from brain signals. We present two cases of study involving a target reaching task in a grid world and using a real mobile robot.
Using frequency-domain features for the generalization of EEG error-related potentials among different tasks
This paper explores the use of low frecuency features to improve the generalization capabilities of the BCIs using error-related potentials.
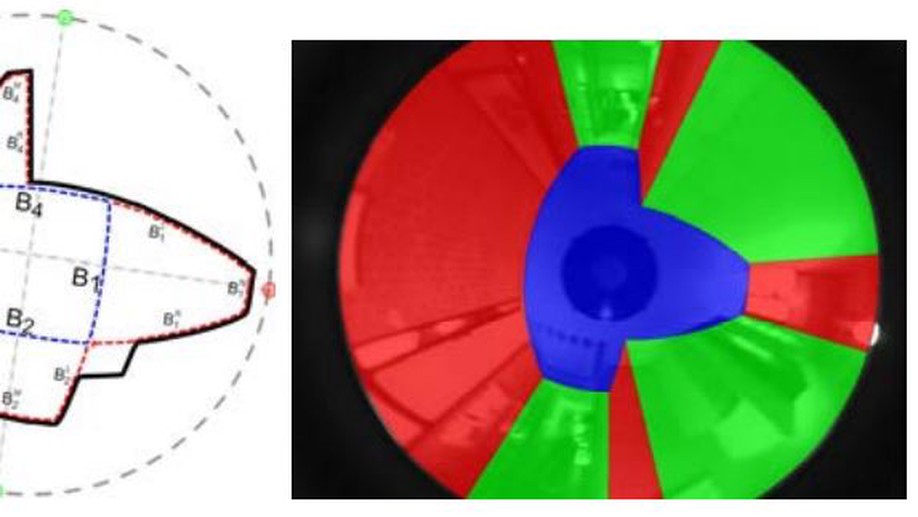
Omnidirectional Vision for Indoor Spatial Layout Recovery
Study on how to recover the spatial layout of a scene from a collection of lines extracted from a single indoor image.